THERMOGRAPHY
THERMOGRAPHY
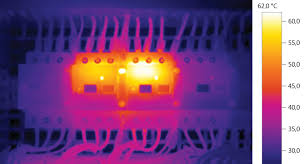
Thermography can easily detect thermal anomalies in electrical equipment. The excessive heat may be due to overloading, improperly sized components, load imbalance, or most commonly, resistance due to poor connections. Mechanical issues can also be detected, such as improper lubrication, misalignment, or any other friction-related issue.
There’s no downside to thermography testing, only benefits. By using infrared technology to help identify potential problems with electrical and mechanical equipment, a facility can take equipment off-line for repair before failure occurs, production is halted, or a fire impacts your business
Thermographic testing of electrical equipment
Thermography is a non-destructive test method that may be used to detect poor connections, unbalanced loads, deteriorated insulation, or other potential problems in energized electrical components. These problems may lead to excess power use, increased maintenance costs, or catastrophic equipment failure resulting in unscheduled service interruptions, equipment damage, or other problems.
Thermography, also called infrared inspection, is based upon the sensing of heat emitted from the surface of an object in the form of infrared radiation. Test instruments are used to detect and convert the infrared radiation into either a temperature value or a thermal image, which can be used to assess the thermal condition of the object at the time of measurement. An infrared camera is one common type of an infrared thermal imaging device.
How can Thermography be used to inspect electrical equipment?
Energized electrical systems generate heat because of electrical resistance. The amount of heat generated is related to the amount of current flowing through the system and the resistance of the individual system components and connections within the system. As components deteriorate, their resistance increases, causing a localized increase in heat. Similarly, a poorly made connection will have higher resistance than a well-made connection, along with a higher temperature profile. Thermography may be used to detect these temperature differences.
What are the benefits of thermographic inspection?
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) estimates that ten percent of the fires occurring in manufacturing properties are related to electrical system failures, such as failure of electrical insulation, terminals, and related components. Additionally, failures can cause employees to be exposed to live electrical circuits, making them susceptible to serious injury or death from electrocution. By detecting high-resistance connections and repairing them, the likelihood of a breakdown of the electrical wires and related components should be reduced.
Other advantages to detecting and repairing these faults are the cost savings from energy conservation and lower outage and repair costs. High resistance in circuits causes an increase in current flow. When current flow is increased, the resulting power consumption will increase. Further, high current draw can cause critical electrical circuit components, such as fuses, circuit breakers, and transformers, to fail prematurely. These failures result in higher maintenance and repair costs, and resultant business interruptions.